Concept
Detection of
- Position
- Shape
- Interaction

Our "Cable-Like-Shape-Sensors", one can imagine as a cable, that is enclosed by a metallic protection hose. The system is elastic and can be mounted to or integrated in objects, which shape should be monitored.
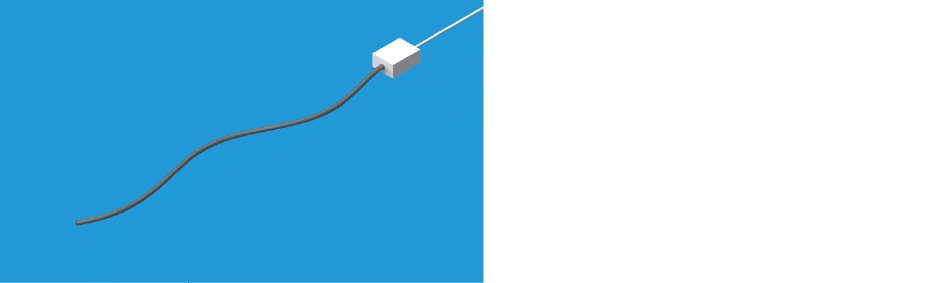
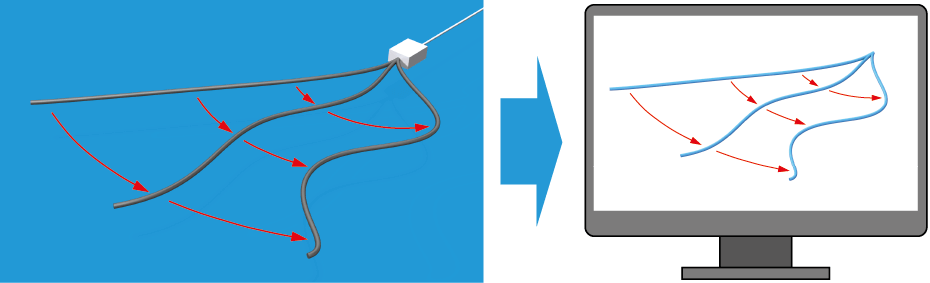
Based on their positioning in space our cable-like shape-sensors create a virtual three-dimensional model of their current layout. This model of the cable's position and shape mirrors precisely the actual cable's position and shape in real-time. This opens up numerous applications.
Function
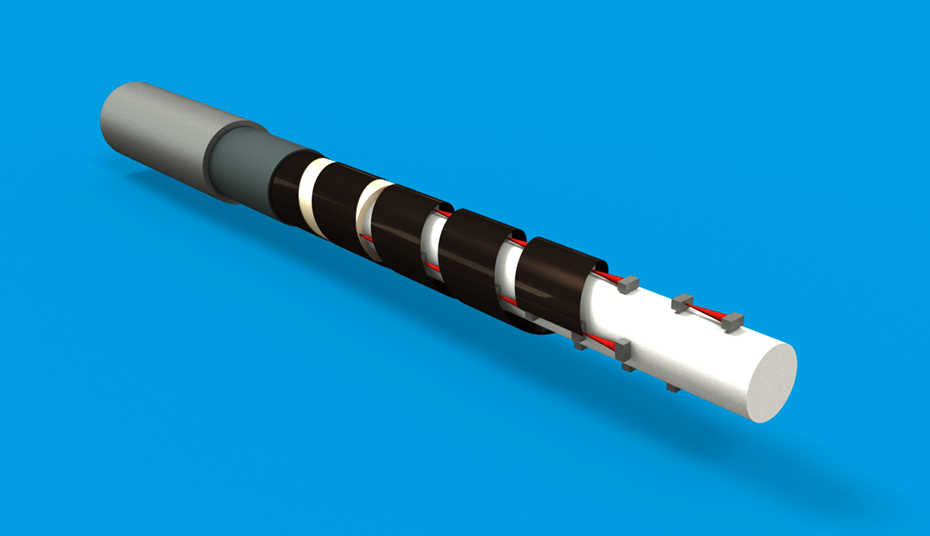
We integrated helically coiled foils into our cable-like shape-sensors. Bends of the cable, therefore, result in changes in the distances between the foil edges. These distances are optically tracked and send to a plotting computer. This distance information is compiled into a virtual model of the cable's shape. Due to the compact construction the sensor delivers a high measuring density and provides space for a usable filling (marked white in the picture), which can host, for example, electric cables, optical fibers or bowden cables.

Possible Applications
For typical applications, the position and orientation at the sensor end are detected.
For some applications, the current shape forming ist relevant too.
For all applications a concurrent monitoring can be realized: If a part of the sensor-array reaches a critical position. If a sensor assumes a critical shape. If parts of the cable approach critical velocities.
Monitoring of Elastic Materials
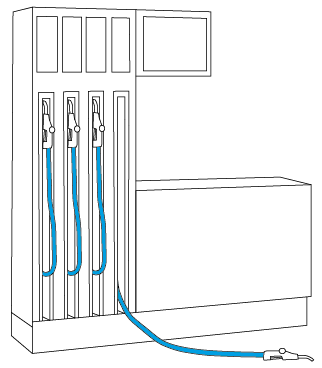
Applications arise wherever flexible connections have to be monitored, for example, cable assemblies or delivery hoses.
Control of heavy Machines
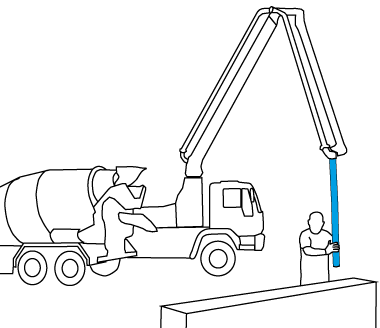
The sensors can also be employed for the guidance of heavy machinery and handling fixtures.
Monitoring of cable delivery tracks
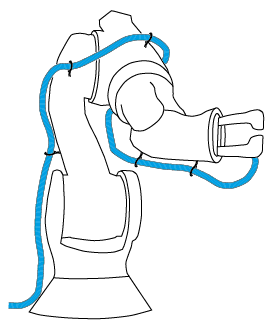
In the case of industrial robots a large portion of their downtimes is due to broken cable connections. Such a machine could be halted beforehand reducing the downtime from hours to minutes.
Targeting of Machine Positions and Movements
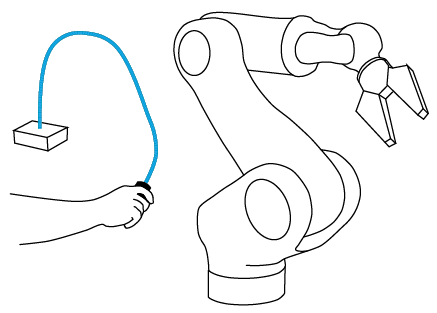
The specification of 3d trajectories of robot movements can be given directly and intuitively.
Control of Complex Machines
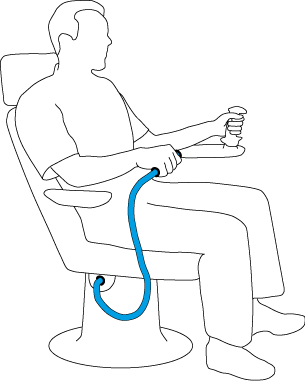
The sensors can be used for interaction. Thereby a direct and intuitive specification of position information with six degrees of freedom is possible. Machines with lots of joints can be controlled intuitively, by directing target positions. The parameter set of the joint angles can be calculatet automatically by inverse kinematics. The troublesome learning of joysticks correspondencies is obsolete.
Monitoring of Assembly Processes
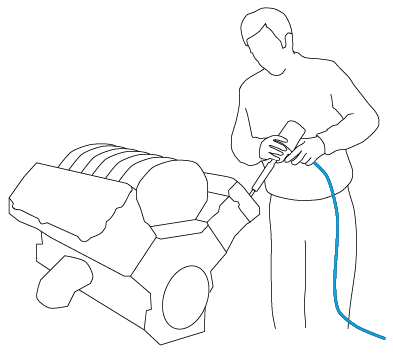
Manual assembly tools can be configured in dependence of their position. A torque wrench may realize different moments of force for different screws.
Automatic Dosage and Documentation
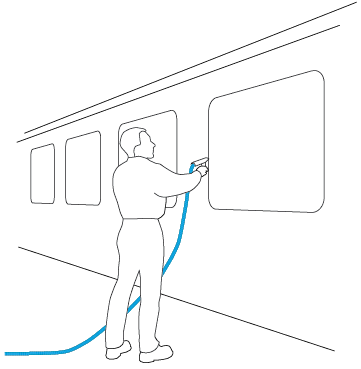
The position information of the sensor shape is updated with high frequency. Thus the velocity at the sensor end can be determined exactly. With this information the automatic dosage of adhesives in dependence of hand movement is feasible. Recordings of trajectories of movement can be used to establish quality of service documentation.
Localizing of Damages in Pipe Systems
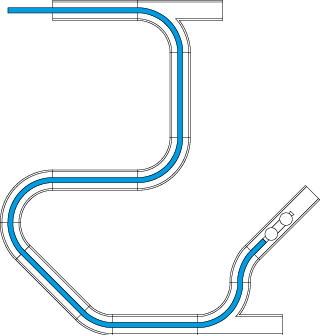
Our sensor technology can be integrated in medical and industrial endoscopes in order to obtain precise positioning information. This increases the manufacturing radiuses only by 1,5mm. Analogously, an employment in so-called rooter systems is possible in order to localize damaged locations.